Wednesday, November 30, 2016
Sunday, November 27, 2016
Thursday, November 24, 2016
happy thanksgiving!
before anyone says anything, i want to say that i am very aware that today, this holiday, is not a thankful day for native americans everywhere who have been wronged, hurt, or attacked in the past, & now, by whites who took over their land.
also, my family doesn't really celebrate thanksgiving all that much other than we make a bit of extra food & i eat pumpkin pie. but after a tntt lock-in that i went to, i was reminded to count my blessings. we made a "Count your blessings" board & i believe that counting your blessings is the same thing as thinking about all that you are thankful for, so here are 10 blessings that i have counted today:
also, my family doesn't really celebrate thanksgiving all that much other than we make a bit of extra food & i eat pumpkin pie. but after a tntt lock-in that i went to, i was reminded to count my blessings. we made a "Count your blessings" board & i believe that counting your blessings is the same thing as thinking about all that you are thankful for, so here are 10 blessings that i have counted today:
i most definitely have countless of blessings in my life- way more than 10- but sometimes i can't remember them all bc i never slow down enough to appreciate what i really have. maybe today, you can take a couple of minutes to count your blessings & remind the people in your life that you are thankful for them.
i am thankful for you.
happy thanksgiving- for those who celebrate it.
also, there is a thanksgiving festival (hoi cho) going on at my church- Our Lady of Lourdes (Lo Duc)- for anyone who is interested! it's from Nov. 25- Nov. 27 & i will be there all 3 days bc i'm in charge of the face painting booth. just putting it out there for anyone who is interested!
Wednesday, November 23, 2016
Monday, November 21, 2016
Sunday, November 13, 2016
Friday, November 11, 2016
ch. 12 | the lymphatic system & immunity
- functions:
- drainage- interstitial fluid is carried through the system & empties into the veins, where it becomes part of the blood plasma again
- transport- moves lipids & lipid-soluble vitamins from digestive tract to blood
- immunity- lymphocytes fight foreign cells
- lymph: when interstitial fluid enters lymphatic vessels; drained by lymphatic or thoracic duct
- primary lymphatic organs: (sites where stem cells divide & develop into B & T cells)
-red bone marrow
-thymus
- T-cells= T lymphocytes (made in red bone marrow & matures in thymus)
- B-cells = B lymphocytes (made & mature in red bone marrow)
- secondary lymphatic organs: (sites where most immune responses occur)
- pathogens: disease-causing organisms
- innate immunity: series of non-specific physical & chemical defenses
-physical barriers: skin, mucous membranes in the nose, upper respiratory tract, intestines, reproductive & urinary systems
-chemical barriers: chemicals w/in various fluids & secretions, killer cells, inflammation, & fever can slow growth of microbes




- adaptive immunity: ability to adapt to specific types of infections or antigens
- cell-mediated immunity: effective against INTRAcellular pathogens, involves T-cells, always involves cells attacking cells
- antibody-mediated immunity: effective against EXTRAcellular pathogens, involves B-cells
-cell-mediated & antibody-mediated immunity often work together to rid the body of antigens
- active immunity: exposed to antigens & body develops antibodies in response; stays for longer periods bc memory cells
- passive immunity: received pre-made antibodies that body can use to defend itself; fleeting
- autoimmunity: immunological response against a person's own tissues (immune cells attack your own body cells)
immune response time speeds up after the initial exposure
-initial response to infection may take several days or weeks
-clonal selection process produces memory cells
-subsequent exposure to the same antigens--> secondary immune response which is stronger
- vaccination: receipt of a vaccine (consists of weakened pathogens)
- acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS): condition in which a person experiences many infections due to progressive destruction of cells of lymphatic system
- human immunodeficiency virus (HIV): virus that causes AIDS
-it is not easy to get infected w it
-cannot be exchanged through casual contact- usually through exchange of body fluids
-symptoms progress SLOWLY & progress in severity
-is a retrovirus (a virus that can convert its RNA into DNA)
Wednesday, November 9, 2016
2016 Election winner: Donald Trump
last night, Donald Trump won the 2016 presidential election.
i have no words to describe all of the feelings that the people of the United States are feeling. personally, i am not very educated in politics but i was not the biggest Trump fan, nor was i the biggest Clinton fan. i don't believe that the U.S. should have felt like it had to choose "between two evils" but there was nothing that i could personally do about it. there are so many shoulda, coulda, woulda's but the reality is that in 2017, Donald Trump is supposed to be our president. that worries me, not because of his ideas, stances, etc. (although those worry me too), but because i don't think that he would be a good, quality leader. i do not think that America is going to look back on this election one day & be proud of this. but it is what it is & all any of us can do from here on out is do better. in the next election, we need to turn it all around. until then, we can only stick together & hope for the best. i know a lot of people are scared/worried for their families, for their friends, & for themselves. i am worried for everyone too. but we can't lose hope in our America bc today's America is the best America that we have had- even if it seems bad. but i believe in us & all we can do is believe in each other. i've seen a lot about the election on social media- facebook, instagram, snapchat, & especially twitter. here are some youtube videos that ya'll should really watch:
i hope that all of you stay safe & remember that you are loved & we can only hope for the best.
Tuesday, November 8, 2016
ch. 11 | the cardiovascular system
overview of the cardiovascular system:
parts of the heart:
 |
| arteries: blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart veins: blood vessels that convey blood from tissues back to the heart |
- arteries= red except at the heart
- veins= blue except at the heart
layers of heart:

blood flow through heart:
- sinoatrial (SA) node: starts a contraction impulse in the right atrium
- resting heart rate: 70-75 beats per minute
- tachycardia: heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate
- bradycardia: abnormally slow heart action
- arrhythmia: an irregular heart rhythm
- myocardial infarction: heart attack
- atherosclerosis: inflammatory disease condition, fatty materials build up in the walls of blood vessels
- systole: contraction phase of cardiac cycle
- diastole: relaxation phase of cardiac cycle
- cardiac cycle lasts about 0.8 seconds
systemic blood vessels:
arteries --> arterioles --> capillaries --> venules --> veins
- aorta is the largest artery of the body
structure of arteries & veins:
- edema: accumulation of interstitial fluid; tissue swelling
- skeletal muscle pump: contractions of skeletal muscles squeeze veins & move blood along
- respiratory pump: pressure changes in thoracic & abdominal cavities during breathing squeeze the abdominal veins & move blood through them
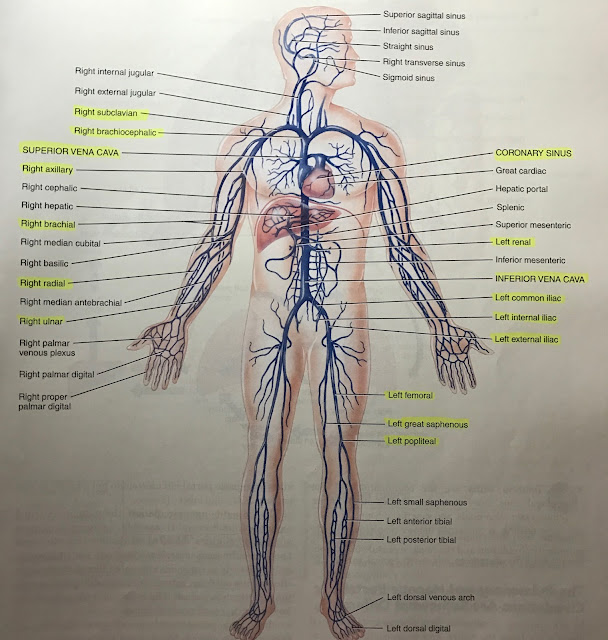
major veins:
- pulmonary circulation:
-pulmonary trunk comes from right ventricle carrying deoxygenated blood
-pulmonary arteries are the only arteries that carry deoxygenated blood
-pulmonary veins are the only veins carry oxygenated blood (from lungs to left atrium)
- heptic portal circulation:
-liver receives blood from heptic portal vein which is an exception to the rule that venous blood returns directly to the heart
-allows liver to process absorbed substances
blood pressure: force exerted by blood against walls of blood vessels due to contraction of heart & influenced by elasticity of vessel walls; measured in "mm Hg"
-normal blood pressure:
-pre-hypertension:

-hypertension: chronic high blood pressure
major arteries:
ch. 10 | the cardiovascular system: blood
major functions:
- transportation: delivers oxygen from lungs to cells, moves carbon dioxide from cells to lungs, carries nutrients/waste products/hormones to destinations
- regulation: maintain steady pH, distributes heat/adjusts body temperature
- protection: forms seals/clots to prevent blood loss, white blood cells fight disease
components of blood:
 |
| plasma: liquid portion of blood formed elements: consist of many types of blood cells erythrocytes= RBCs leukocytes= WBCs |
- RBCs- deliver oxygen
- WBCs- fight foreign bodies
- platelets- clot
origin & development of blood cells:
- hemopoiesis: process of making formed elements in red bone marrow
- hemostasis: stoppage of bleeding
- thrombus: small clot that forms in an unbroken vessel & dissolves spontaneously
- embolus: clot that breaks off & travels through cardiovascular system
- RBCs are dismantled in spleen/liver/red bone marrow
- the hormone erythropoietin stimulates erythropoiesis (red blood cell formation) in red bone marrow
- leukocytosis: above average/increase in WBC count
- leukopenia: below average/reduction in WBC count
- agglutination: RBCs clump together
- hemolysis: RBSs burst
- polycythemia: disorder characterized by too many RBCs
- anemia: condition of blood in which there are too few RBCs
- leukemia: red bone marrow cancers in which abnormal white blood cells multiply uncontrollably
- neutrophil: most abundant type of WBC in mammals
- monocyte: WBC w simple oval nucleus and clear, grayish cytoplasm
Sunday, November 6, 2016
ch. 9 | the endocrine system
- endocrine system: system of glands & hormones secreting cells that regulate body functions through chemical messages (hormones)
- endocrine glands: secrete a chemical signal directly into the bloodstream
- exocrine glands: secrete a chemical signal through ducts or tubes
- 2 types of hormones:
1. steroid: dissolves in fats or lipids; go directly into the target cell
2. nonsteroid: dissolves in water; bind to receptors on target cell membrane
glands:
- pituitary gland: influenced by the hypothalamus
- anterior pituitary
-hormones:
thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)- controls metabolism
follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)- promotes egg & sperm development
luteinizing hormone (LH)- controls ovulation & production of estrogen/testosterone
adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)- breaks down proteins/fats, forms glucose
-disorders from too little/too much secretion of human growth hormone (hGH):
pituitary dwarfism: too little hGH prior to puberty, does not grow to normal height
gigantism: too much hGH prior to puberty, taller-than-normal height
acromegaly: excess secretion of hGH after puberty, condition in which long bones can no longer grow but bones in hands/feet/face/jaw thicken & grow longer
- posterior pituitary
-axons & terminals of specialized nerve cells from hypothalamus
-hormones:
oxytocin: stimulates contraction of uterus during birth, stimulates lactation
antidiuretic hormone (ADH): acts to conserve body water & increases blood pressure
- thyroid gland: regulates metabolism
-calcitonin: hormone secreted by cells of thyroid gland that inhibit osteoclast activity & lowers blood calcium levels
- parathyroid gland: regulate calcium levels, embedded in posterior of thyroid gland

-secrete PTH which acts on osteoclasts to release calcium & reduce calcium excretion & to release calcitriol (increases blood calcium levels)
- pancreas: regulate blood sugar levels

-alpha cells: secrete glucagon
-beta cells: secrete insulin
-secretions of glucagon & insulin are coordinated to prevent blood glucose levels from rising too much after a meal & falling too much btwn meals
-hypoglycemia: blood glucose levels are below normal
-hyperglycemia: blood glucose levels are above normal
-diabetes mellitus: elevated blood glucose levels & impairs glucose tolerance
type I: lack of insulin; immune sys. destroyed by beta cells; develops early in life (juvenile diabetes)
type II: decreased sensitivity of target cells to insulin; develops later in life (lifestyle diabetes)
- adrenal glands: sit on top of each of the kidneys

-types of steroid hormones secreted:
mineralocorticoids: outer zone of adrenal cortex; regulate mineral composition of the blood
glucocorticoids: middle layer of adrenal cortex; regulate energy balance
androgens: inner zone of adrenal cortex; influence sexual characteristics & behaviors
epinephrine & norepinephrine: adrenal medulla; regulate body's response to stress & exercise
- pineal gland: sets daily sleep/wake cycles
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)