functions of skeletal system:
- support- provides framework to support soft tissues
- protection- protects internal organs from injury
- movement- muscles provide force while bones serve as levers
- mineral homeostasis- bone tissue stores calcium & phosphorus
- blood cell protection- red bone marrow goes through hemopoiesis (blood cell production)
- triglyceride storage- yellow bone marrow is made of adipose cells which stores triglycerides
- the adult skeletal system is made of 206 different bones
4 types of bones:
- long- longer than they are wide, knobby ends, curved structure (arms, legs, fingers, toes)
- short- equal in width & length (wrists, ankles)
- flat- thin, provide protection & surfaces for muscle attachments (skull, sternum, ribs)
- irregular- complex shapes (face, vertebral column)
parts of a long bone:
- diaphysis: middle of long bone, hollow
has a hollow chamber called medullary cavity
contains yellow marrow which stores fat - epiphysis: end of long bone, solid
covered by articular cartilage
- periosteum: tough membrane covering the bone
- osteoblasts: build extracellular matrix; when entrapped in matrix--> becomes osteocytes
- osteoclasts: digest & reabsorb proteins & minerals from matrix
axial skeleton: 80 bones
- foramen: holes in a bone for passage of vessels or nerves
- suture: immovable joint that joins most of the skull bones
- fontanels: soft spots on a baby's head- allow the bones of skull to compress as baby is born & provide room for brain to grow
- hyoid bone: located in the neck, suspended from styloid process; supports tongue, stabilizes airways, provides attachment points for tongue/neck/pharyngeal muscles
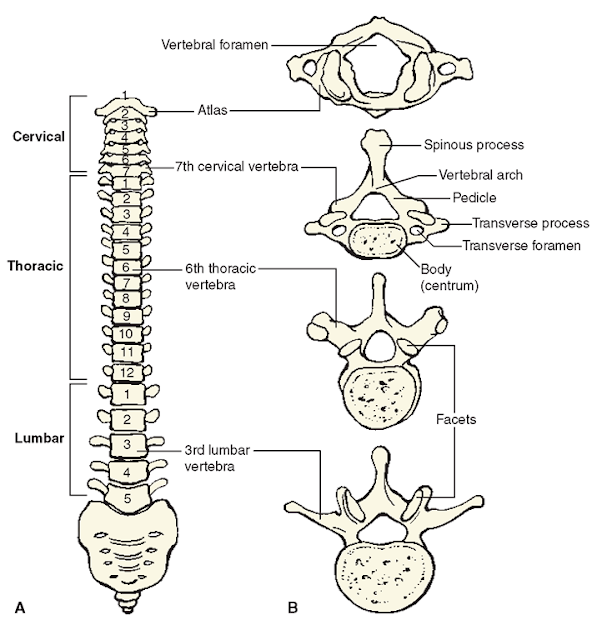
- types of vertebrae:
-cervical: (7) has 3 openings, neck region
-thoracic: (12) posterior to chest, attachment points for ribs
-lumbar: (5) form lower back
-sacrum: (5 fused into 1) posterior wall of pelvis
-coccyx: (4 fused into 1) tailbone
- parts of a vertebrae:
- clavicle & scapula:

- humerus:
- radius & ulna:
- hand:
- pelvic girdle:
- femur:
- knee:
- fibula & tibia:
- foot:
types of joints:
- hinge joint:
- pivot joint:
- plane joint:
- ball-and-socket:
movements:
- dorsiflexion: instep of foot moved toward shin
- plantar flexion: toes pointed downward
- flexion: decreases angle btwn bones
- extension: increases angle btwn bones
- elevation: upward
- depression: downward
- lateral rotation: turn away from midline (horizontally)
- medial rotation: turn towards midline (horizontally)
- abduction: move away from midline (vertically)
- adduction: move towards midline (vertically)
joints classified structurally:
- fibrous: no movement
- cartilaginous:
- synovial: freely movable

































No comments:
Post a Comment