overview of the cardiovascular system:
parts of the heart:
 |
| arteries: blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart veins: blood vessels that convey blood from tissues back to the heart |
- arteries= red except at the heart
- veins= blue except at the heart
layers of heart:

blood flow through heart:
- sinoatrial (SA) node: starts a contraction impulse in the right atrium
- resting heart rate: 70-75 beats per minute
- tachycardia: heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate
- bradycardia: abnormally slow heart action
- arrhythmia: an irregular heart rhythm
- myocardial infarction: heart attack
- atherosclerosis: inflammatory disease condition, fatty materials build up in the walls of blood vessels
- systole: contraction phase of cardiac cycle
- diastole: relaxation phase of cardiac cycle
- cardiac cycle lasts about 0.8 seconds
systemic blood vessels:
arteries --> arterioles --> capillaries --> venules --> veins
- aorta is the largest artery of the body
structure of arteries & veins:
- edema: accumulation of interstitial fluid; tissue swelling
- skeletal muscle pump: contractions of skeletal muscles squeeze veins & move blood along
- respiratory pump: pressure changes in thoracic & abdominal cavities during breathing squeeze the abdominal veins & move blood through them
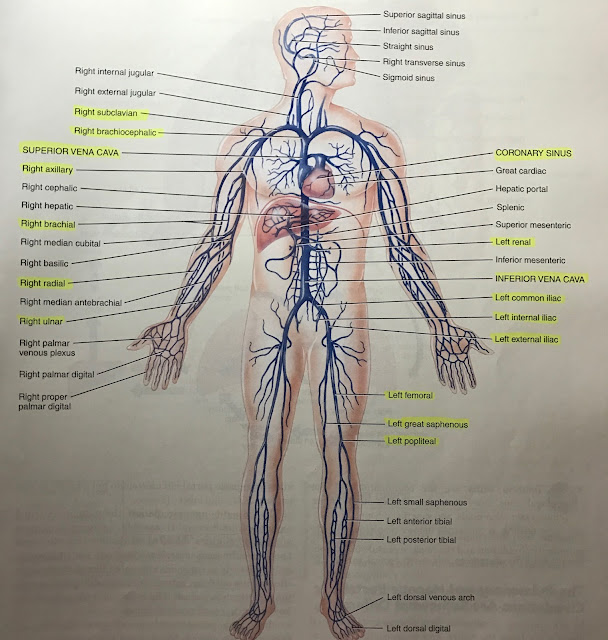
major veins:
- pulmonary circulation:
-pulmonary trunk comes from right ventricle carrying deoxygenated blood
-pulmonary arteries are the only arteries that carry deoxygenated blood
-pulmonary veins are the only veins carry oxygenated blood (from lungs to left atrium)
- heptic portal circulation:
-liver receives blood from heptic portal vein which is an exception to the rule that venous blood returns directly to the heart
-allows liver to process absorbed substances
blood pressure: force exerted by blood against walls of blood vessels due to contraction of heart & influenced by elasticity of vessel walls; measured in "mm Hg"
-normal blood pressure:
-pre-hypertension:

-hypertension: chronic high blood pressure
major arteries:










No comments:
Post a Comment