it's hard to post playlists w/o repeats of last month's songs bc i just keep listening to the same songs
Thursday, September 29, 2016
Sunday, September 25, 2016
ch. 5 | the skeletal system
functions of skeletal system:
- support- provides framework to support soft tissues
- protection- protects internal organs from injury
- movement- muscles provide force while bones serve as levers
- mineral homeostasis- bone tissue stores calcium & phosphorus
- blood cell protection- red bone marrow goes through hemopoiesis (blood cell production)
- triglyceride storage- yellow bone marrow is made of adipose cells which stores triglycerides
- the adult skeletal system is made of 206 different bones
4 types of bones:
- long- longer than they are wide, knobby ends, curved structure (arms, legs, fingers, toes)
- short- equal in width & length (wrists, ankles)
- flat- thin, provide protection & surfaces for muscle attachments (skull, sternum, ribs)
- irregular- complex shapes (face, vertebral column)
parts of a long bone:
- diaphysis: middle of long bone, hollow
has a hollow chamber called medullary cavity
contains yellow marrow which stores fat - epiphysis: end of long bone, solid
covered by articular cartilage
- periosteum: tough membrane covering the bone
- osteoblasts: build extracellular matrix; when entrapped in matrix--> becomes osteocytes
- osteoclasts: digest & reabsorb proteins & minerals from matrix
axial skeleton: 80 bones
- foramen: holes in a bone for passage of vessels or nerves
- suture: immovable joint that joins most of the skull bones
- fontanels: soft spots on a baby's head- allow the bones of skull to compress as baby is born & provide room for brain to grow
- hyoid bone: located in the neck, suspended from styloid process; supports tongue, stabilizes airways, provides attachment points for tongue/neck/pharyngeal muscles
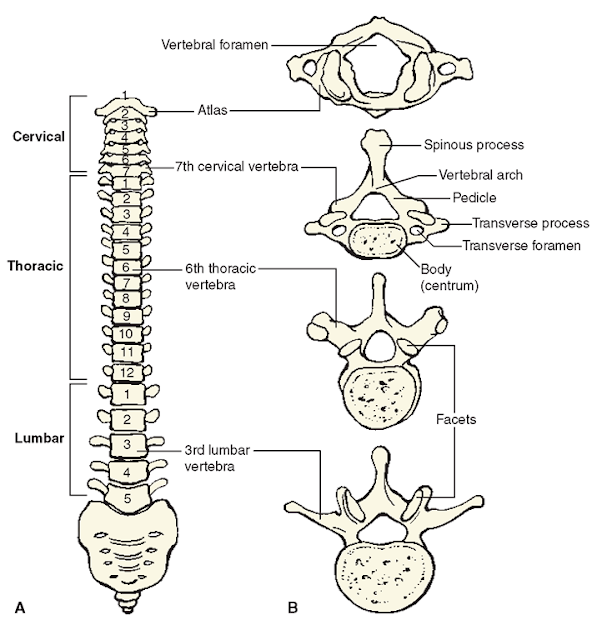
- types of vertebrae:
-cervical: (7) has 3 openings, neck region
-thoracic: (12) posterior to chest, attachment points for ribs
-lumbar: (5) form lower back
-sacrum: (5 fused into 1) posterior wall of pelvis
-coccyx: (4 fused into 1) tailbone
- parts of a vertebrae:
- clavicle & scapula:

- humerus:
- radius & ulna:
- hand:
- pelvic girdle:
- femur:
- knee:
- fibula & tibia:
- foot:
types of joints:
- hinge joint:
- pivot joint:
- plane joint:
- ball-and-socket:
movements:
- dorsiflexion: instep of foot moved toward shin
- plantar flexion: toes pointed downward
- flexion: decreases angle btwn bones
- extension: increases angle btwn bones
- elevation: upward
- depression: downward
- lateral rotation: turn away from midline (horizontally)
- medial rotation: turn towards midline (horizontally)
- abduction: move away from midline (vertically)
- adduction: move towards midline (vertically)
joints classified structurally:
- fibrous: no movement
- cartilaginous:
- synovial: freely movable
Ch. 8 | the legislative branch
legislative functions:
- enact bills
- adopt resolutions
- proposing constitutional amendments
- adopting budgets for state government
- levying taxes
- redistricting
- impeaching & removing executive & judicial officials
election & terms of office
- representatives elected for 2 years
- senators elected for 4 years
- terms begin in January of odd-numbered years
sessions
regular sessions: session of TX legislature that is constitutionally mandated
- begins on second Tuesday in January of odd-numbered years
- lasts for a max. of 140 days
- Austin economy benefits bc legislators & lobbyists spend money for housing & entertainment
special sessions: legislative session called by governor
- limited to no more than 30 days
- legislature may only consider matters placed before it by governor
- costly to taxpayers
- unpopular w legislators
districting
- states divided into districts to provide equal representation
redistricting: redrawing boundaries
- districts redrawn due to migration, births, & deaths
Reynolds v. Sims: "the seats in both houses of a bicameral state legislature must be apportioned on a population basis"
Kilgarlin v. Martin: "one person, one vote"
gerrymandering: drawing boundaries of districts to include/exclude certain groups to affect election
single-member district: area that elects only one representative to a policymaking body
- reduce campaign costs
- increase probability that more African American & Latino candidates will be elected
multimember district: all voters participate in election of 2+ representatives to policymaking body
Perez v. Perry: lawsuits consolidated into one case, claimed the redistricting plans discriminated against Latinos & African Americans
Shelby County v. Holder: automatic pre-clearance requirements of the Voting Rights Act were no longer applicable
TX legislatures must meet state constitutional qualifications:
- U.S. citizen
- qualified voter
- one year residence in district to be represented preceding election
- House: 2 years of TX residence preceding election; Senate: 5 years
- House: 21 years old; Senate: 26 years old
gender & ethnic classifications
- Anglo men dominate TX legislature
- general disrespect of female legislators
- African American & Latinos underrepresented
political party affiliation
- 2011: Republications achieved super-majority status in House of Representatives
- Central city residents usually elect African American & Latino Democrats
- Republican senators & representatives get support from rural & suburban Anglo voters
education & occupation
- most positions of leadership call for college credentials
- most legislators are attorneys, business owners, or managers
- laborers have held almost no seats
religious affiliation
- legislators' religious beliefs may play role in forming public policy
- most numerous (in order): Baptists, Methodists, & Episcopalians
legislative experience
- terms of turnover (first-termers replacing experienced) or tenure (years served)
- incumbent more likely to win an election
- TX does not have term limits for legislators
TX legislators receive low pay, reasonable allowances, & generous retirement pension
pay & per diem allowance
- Texas Ethics Commission sets per diem expense allowance
- TX voters must approve all recommended salary increases
expense allowances
- at the beginning of each session, each chamber authorizes contingent expense allowances
- use money to cover cost of work-related travel, postage, office operations, staff salaries
retirement pension
- Texas State Employees Retirement Act of 1975: legislators contribute 8% of their state salaries to retirement fund
- many legislators do not serve long enough to qualify for a pension
president of Senate: the lieutenant governor:
- not a member of the state Senate
- presides over most sessions & plays leading role in legislative matters
- first in line of succession in event of death/resignation/removal of governor
- powers granted by Senate rules
- Senate elects president pro tempore= presides when lieutenant governor is absent/disabled
presiding officer of the House of Representatives: Speaker of the House:
- candidates must file w Texas Ethics Commission
presiding officers appoint committee chairs & determine the committees to which bills are referred
house committees
substantive committee: appointed by House Speaker
- considers bills & resolutions related to subject identified by its name
- may recommend passage of proposed legislation to appropriate calendars committee
procedural committee: consider bills & resolutions relating to procedural legislative matters
select committee: created by House Speaker or lieutenant governor; may consider legislation that crosses committee jurisdictional lines/may conduct special studies
interim committee: House/Senate committee appointed by Speaker or lieutenant governor to study important policy issue btwn regular sessions
senate committees
standing committee: appointed by lieutenant governor for purpose of considering proposed bills ^ resolutions before possible floor debate & voting
legislative caucuses: legislators who try to maximize influence over issues of special interest
- party caucuses: take policy positions on issues & promote unity among members
- racial/ethnic caucuses: organize & form voting blocs to maximize their power
- ideological caucuses: conservative & liberal caucuses reflect opposing views on most issues
- bipartisan caucuses: framed around specific issues
along w their powers, lawmakers have immunities from prosecution
making public policy
- most typical exercise of legislative power
- passing bills & adopting resolutions
simple resolution: requires action by one legislative chamber only
concurrent resolution: adopted by House & Senate majorities then approved by governor
joint resolution: majority vote in each house when used to ratify an amendment
bill: proposed law or statute
- special bill: makes exception to general laws for specific individual/class/corporation
- general bill: apply to all people/property
- local bill: creates/affects single unity of local government
constitutional amendment power
- members of either chamber can introduce joint resolution to amend TX constitution
- approved by 2/3rds majority vote --> proposal is made
administrative & investigative powers
oversight: requires reports from state agencies concerning their operations
- state auditor gives info to House & Senate about use of state funds by administrative agencies
Sunset Advisory Commission: recommends continuation/merger/division/abolition of agencies
senatorial courtesy: Senate rejects an appointment if appointee is declared "personally objectionable" by senator representing the district in which the appointee resiedes
impeachment & removal powers
- House of Representatives has power to impeach all elected state judges & justices
impeachment: brings charges leading to possible removal of certain officials
immunities
- can't be sued for slander
- not held accountable for statements made in speech or debate during legislative proceeding
- may not be arrested while attending legislative session or traveling to/from meeting place
each chamber adopts its own set of rules at the beginning of every regular session
parliamentarian: an expert on rules of order who sits at left of the presiding officer in House or Senate & provides advice on procedural questions
how a bill becomes a law
1. introduction in the House
- companion bill: filed in one house but identical/similar to a bill filed in other chamber- speeds passage of bill bc committee consideration may take place simultaneously in both houses
2. first reading (House) & referral to committee
3. house committee consideration & report
- bill analysis that summarizes important provisions of bill
- ghost voting: prohibited practice of one representative pressing the voting button of another member who is absent (unless given permission)
- chubbing: representatives engage in lengthy debate for the purpose of using time & preventing a vote on a bill that they oppose
5. third reading (House)
6. first reading (Senate)
7. Senate committee consideration & report
- two-thirds rule: procedural device to control bringing bills to the Senate floor for debate
8. second reading (Senate)
9. third reading (Senate)
10. return to the House
11. conference committee
- committee composed of representatives & senators appointed to reach agreement on a disputed bill & recommend changes acceptable to both chambers
12. conference committee report
13. enrollment
- bill is stamped "enrolled" & report is presented to the House
14. signatures of chief clerk & speaker
15. signatures of secretary of Senate & lieutenant governor
16. action by governor
- 3 options:
- sign bill
- allow it to remain unsigned for 10 days- becomes law w/o chief executive's signature
- w/in 10 day period, veto- return to House, unsigned, w reason for veto
influences w/in legislative environment:
the Texas Legislative Council
- authorizes special research projects
- bill drafting
- advice for legislators
- legislative research & writing
- publishing & document distribution
- interim study committee research support
- demograpic & statistical date compilation & analysis
- computer mapping & analysis
the House Research Organization
- independent of House leadership
- produces reports on policy issues & House procedures
- prepares Daily Floor Report for each day the legislature is in session
- analyze important bills to be considered
- provide summary of bill content & presenting arguments for/against each bill
- publishes report on session's important bills & resolutions
the Senate Research Center
- analyzes bills under consideration by Senate
- conducts research on diverse issues
- responds to requests from Senate members for research & info
the Center for Public Policy Priorities
- independent nonprofit
- focus on problems of low/moderate income families
the Texas Public Policy Foundation
- research on issues supporting limited government, free enterprise, private property rights, etc.
Saturday, September 24, 2016
Sunday, September 18, 2016
Ch. 2 | federalism & the Texas constitution
federalism: structure of government characterized by the division of powers btwn a national government & associated regional governments
10th amendment: "the powers not delegated by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States, respectively, or to the people"
national supremacy clause: emphasizes that the U.S. constitution & acts of Congress must prevail over state constitutions & laws enacted by state legislatures
delegated powers: (of the national government) listed in the U.S. constitution, article 1, section 8
-regulate interstate & foreign commerce
-borrow & coin money
-establish post offices & post roads
-declare war
-raise & support armies
-provide & maintain a navy
-levy & collect taxes
-establish uniform rules of naturalization
implied powers: power to "make all laws which shall be necessary & proper"
constitutional guarantees: (under the rights & protections of U.S. constitution)
-a state cannot divide itself nor combine w another state w/o consent of Congress
-each state guaranteed a republican form of gov. (representative gov. w elected lawmakers)
-each state guaranteed 2 senators & 1 member of House of Representatives
-all states participate in presidential elections through the electoral college
-all states participate in approving/rejecting proposed amendments
-each state entitled to protection against invasion & domestic violence
-TX is assured that trials by federal courts for crimes committed in TX will be conducted in TX
privileges & immunities: Article IV & 11th amendment guarantees citizens of every state protection by the government, enjoyment of life & liberty, right to acquire & possess property, right to leave & enter any state, & right to use of courts
full faith & credit clause: most legislative enactments, state constitutions, deeds, wills, marriages, divorces, etc. of another state must be officially recognized in other states
reserved powers: (of the states)
-police: protection of citizens' health/morals/safety/convenience
-taxing: raising revenue to pay salaries of state employees, meet other gov. costs
-proprietary: public ownership of property
-eminent domain: taking private property at fair price for public use
federal grants-in-aid: money to help states provide needed facilities & services
devolution: decline in national control over state governments = more power for states
block grants: allows state flexibility in spending for a program
Texas Constitution (1876) is the main source of power for TX government
^ has been amended no fewer than 483 times
TX has been governed by its state constitutions of 1845, 1861, 1866, 1869, & 1876
Texas Grange: farmers' organization committed to limited gov. & spending
constitutional amendment process: (for changing the TX constitution) an amendment is proposed by 2/3rds vote of each chamber of legislature & approved by majority of votes in election
constitutional amendment election: voters asked to approve proposed constitutional amendments
initiative: citizen-drafted measure proposed by a specific number of voters that becomes law if approved by popular vote
constitutional revision: extensive or complete rewriting of a constitution
November 1975 was the last time that voters were presented w a wholesale constitutional revision proposal from the state legislature
Texas Bill of Rights: (article 1 of TX constitution) guarantees protections for:
-people & their property against arbitrary actions by state & local governments
-freedom of speech
-freedom of press
-freedom of religion
-freedom of assembly
-freedom of petition
-rights of criminals & victims
-equal rights for women
Texas Equal Legal Rights Amendment: guarantees equality of sex/race/color/creed/etc.
the TX constitution contains constitutional rights not found in the U.S. constitution
separation of powers: (article II) law-making/enforcing/interpreting= separate branches of gov.
-Legislative department: (article III) bicameral legislature-House of Representatives & Senate
-Executive department: (article IV) governor= Chief executive officer of the State
-Judicial department: (article V) TX has bifurcated court system- 2 courts of final appeal: Supreme Court of TX (civil cases) & Court of Criminal Appeals (criminal cases)
suffrage: the right to vote (article VI)
local government: counties, municipalities, school districts, etc. that provide a range of services
other articles:
-education
-taxation & revenue
-public lands & land office
-impeachment
-general provisions
-mode of amendment
10th amendment: "the powers not delegated by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the States, are reserved to the States, respectively, or to the people"
national supremacy clause: emphasizes that the U.S. constitution & acts of Congress must prevail over state constitutions & laws enacted by state legislatures
delegated powers: (of the national government) listed in the U.S. constitution, article 1, section 8
-regulate interstate & foreign commerce
-borrow & coin money
-establish post offices & post roads
-declare war
-raise & support armies
-provide & maintain a navy
-levy & collect taxes
-establish uniform rules of naturalization
implied powers: power to "make all laws which shall be necessary & proper"
constitutional guarantees: (under the rights & protections of U.S. constitution)
-a state cannot divide itself nor combine w another state w/o consent of Congress
-each state guaranteed a republican form of gov. (representative gov. w elected lawmakers)
-each state guaranteed 2 senators & 1 member of House of Representatives
-all states participate in presidential elections through the electoral college
-all states participate in approving/rejecting proposed amendments
-each state entitled to protection against invasion & domestic violence
-TX is assured that trials by federal courts for crimes committed in TX will be conducted in TX
privileges & immunities: Article IV & 11th amendment guarantees citizens of every state protection by the government, enjoyment of life & liberty, right to acquire & possess property, right to leave & enter any state, & right to use of courts
full faith & credit clause: most legislative enactments, state constitutions, deeds, wills, marriages, divorces, etc. of another state must be officially recognized in other states
reserved powers: (of the states)
-police: protection of citizens' health/morals/safety/convenience
-taxing: raising revenue to pay salaries of state employees, meet other gov. costs
-proprietary: public ownership of property
-eminent domain: taking private property at fair price for public use
federal grants-in-aid: money to help states provide needed facilities & services
devolution: decline in national control over state governments = more power for states
block grants: allows state flexibility in spending for a program
Texas Constitution (1876) is the main source of power for TX government
^ has been amended no fewer than 483 times
TX has been governed by its state constitutions of 1845, 1861, 1866, 1869, & 1876
Texas Grange: farmers' organization committed to limited gov. & spending
constitutional amendment process: (for changing the TX constitution) an amendment is proposed by 2/3rds vote of each chamber of legislature & approved by majority of votes in election
constitutional amendment election: voters asked to approve proposed constitutional amendments
initiative: citizen-drafted measure proposed by a specific number of voters that becomes law if approved by popular vote
constitutional revision: extensive or complete rewriting of a constitution
November 1975 was the last time that voters were presented w a wholesale constitutional revision proposal from the state legislature
Texas Bill of Rights: (article 1 of TX constitution) guarantees protections for:
-people & their property against arbitrary actions by state & local governments
-freedom of speech
-freedom of press
-freedom of religion
-freedom of assembly
-freedom of petition
-rights of criminals & victims
-equal rights for women
Texas Equal Legal Rights Amendment: guarantees equality of sex/race/color/creed/etc.
the TX constitution contains constitutional rights not found in the U.S. constitution
separation of powers: (article II) law-making/enforcing/interpreting= separate branches of gov.
-Legislative department: (article III) bicameral legislature-House of Representatives & Senate
-Executive department: (article IV) governor= Chief executive officer of the State
-Judicial department: (article V) TX has bifurcated court system- 2 courts of final appeal: Supreme Court of TX (civil cases) & Court of Criminal Appeals (criminal cases)
suffrage: the right to vote (article VI)
local government: counties, municipalities, school districts, etc. that provide a range of services
other articles:
-education
-taxation & revenue
-public lands & land office
-impeachment
-general provisions
-mode of amendment
Ch. 4 | the integumentary system
integumentary system: composed of skin, hair, oil, sweat glands, nails, sensory receptors
skin/cutaneous membrane; covers external surface of the body
epidermis: superficial, thinner layer of skin made of epithelial tissue
layers:
dermis: deeper, thicker layer of skin made of connective tissue
skin color is caused by pigments
- melanin: dark black/brown/yellow pigment
- hemoglobin: red pigment
- carotene: yellow/orange pigment
hair protects the skin & other structures of the body
parts:
- shaft: above skin surface
- root: below surface
- hair follicle: surrounds the root
- hair root plexuses: nerve endings that surround hair follicles
androgens: masculinizing sex hormone produced by testes in males & adrenal cortex in both genders
glands produce secretions that perform a variety of functions
- sebaceous: secrete sebum (oily substance), softens skin, prevents hair from drying out
- sudoriferous: sweat glands
-eccrine: all over the body- regulates body temperature
-apocrine: in axillary & pubic regions
- ceruminous: sweat glands in ear canal & outer ear, secrete cerumen (earwax)
parts of the nail:
 |
| dividing cells of a nail are located in nail matrix |
skin plays a number of roles in the body:
- regulates body temperature
- forms a protective barrier for the internal organs
- absorbs & excretes substances through its surface
- plays a role in calcium homeostasis
edema: abnormal accumulation of interstitial fluid
burns:
1st degree: damages epidermis; redness, mild pain
2nd degree: damages epidermis & superficial part of dermis; blisters, edema
3rd degree: damages epidermis & dermis; marble-white to black color
4th degree: damages epidermis, dermis, & additional soft tissue underlying the skin
rule of nines: used to estimate the surface area affected by burns in an adult
skin cancers can develop from repeated exposure to UV radiation:
- basal cell carcinoma (78% of all skin cancers)
- squamous cell carcinoma (20% of all skin cancers)
- malignant melanoma (2% of all skin cancers)
Thursday, September 15, 2016
Ch. 3 | cells & tissues
cell parts:
organelle: membrane-bound structure w/in a cell that carries out specific functions
cytoplasm: area btwn plasma membrane & nucleus; contains organelles & cytosol (fluid inside cell)
nucleus: houses genetic material
functions:
functions:

cytoplasm: area btwn plasma membrane & nucleus; contains organelles & cytosol (fluid inside cell)
nucleus: houses genetic material
functions:
- controls cellular structure
- directs cellular activities
- produces ribosomes in nucleoli
functions:
- barrier separating inside & outside of cell
- controls flow of substances into & out of cell
- helps identify the cell to other cells
- participates in intercellular signaling
centrosomes: consists of centriole pairs
function:
- plays a role in cell division
ribosomes: made of RNA & proteins
functions:
- make new proteins
smooth endoplasmic reticulum: doesn't have ribosomes
functions:
- synthesizes fatty acids & steriods
- inactivates/detoxifies drugs & harmful substances
- stores & releases calcium ions
rough endoplasmic reticulum: contains ribosomes on walls
function:
- make proteins
golgi complex: array of flat membrane sacs
functions:
- modifies/sorts/packages/transport proteins received from rough ER
- transfer proteins to their destinations
mitochondria: folded inner membrane surrounded by smooth outer membrane
functions:
- generates ATP/energy
membranes: transport substances
2 fluid compartments:
- intracellular fluid (inside the cell)
- extracellular fluid (outside the cell); different locations = different names:
-interstitial fluid: btwn cells w/in a tissue
-plasma: w/in blood vessels
-lymph: w/in lymphatic vessels
-cerebrospinal fluid: surrounding brain & spinal cord
-plasma: w/in blood vessels
-lymph: w/in lymphatic vessels
-cerebrospinal fluid: surrounding brain & spinal cord
concentration: amount of solute dissolved in a given volume of solvent
concentration gradient: difference in concentration of substance btwn 2 areas
types of transport:
- passive: movement w/o using energy
- diffusion- substances move high-->low concentration (down concentration gradient)
- facilitated- diffusion using a channel/pore/carrier
- osmosis- diffusion of water
-hypotonic: solution has lower solute concentration than cytosol = cell swells
-isotonic: solution has same solute concentration as cytosol = no net movement
-hypertonic: solution has higher solute concentration than cytosol = shrivels up
- active: energy is used to move substances across a membrane against concentration gradient
protein synthesis: complex process in which proteins are made
TRANSCRIPTION:
1. gene on DNA strand is copied into mRNA (messenger RNA)
2. mRNA is transported out of the nucleus & into ribosomes
TRANSLATION:
1. gene on DNA strand is copied into mRNA (messenger RNA)
2. mRNA is transported out of the nucleus & into ribosomes
TRANSLATION:
3. ribosomes read mRNA so tRNA (transfer RNA) knows which amino acids to bring
4. ribosomes join amino acids together as required by DNA
5. ribosome falls apart & releases newly made protein
daughter cell: either of the two identical cells that form when a cell divides4. ribosomes join amino acids together as required by DNA
5. ribosome falls apart & releases newly made protein
cell division functions:
- cell renewal
- cell repair
- cell growth
- reproduction
types of cell division:
- mitosis: somatic cell division
 |
parts of interphase: (resting phase)
1. G1- growth phase where proteins are synthesized
2. S- DNA is replicated
3. G2- another growth phase where proteins are made
|
- cytokinesis: cytoplasm division
- meiosis: gamete cell division
tissues: groups of cells working together to perform a specific function
2 components found in tissue:
- cells
- extracellular matrix (which has 2 components: ground substance & protein fibers)
4 basic types of tissues:
1. epithelial: protection, covers body surfaces, form glands, lines body cavities/hollow organs/ducts
- epithelial cell shapes & layers:
 |
| simple:absorption/secretion stratified: protection |
locations:
Simple squamous- blood vessels, lining of heart (diffusion & filtration)
Simple cuboidal- ovary linings, eye surfaces (secretion & absorption)
Simple columnar- lining of digestive tract (absorption)
Stratified squamous- skin (upper layers), lining of vagina, mouth (protects underlying cells)
Transitional- lining of urinary bladder (specialized)
Pseudostratified columnar- lines respiratory passageways
Simple squamous- blood vessels, lining of heart (diffusion & filtration)
Simple cuboidal- ovary linings, eye surfaces (secretion & absorption)
Simple columnar- lining of digestive tract (absorption)
Stratified squamous- skin (upper layers), lining of vagina, mouth (protects underlying cells)
Transitional- lining of urinary bladder (specialized)
Pseudostratified columnar- lines respiratory passageways
2. connective: binds/protects/supports body & organs
locations:
- Areolar – skin (provides strength/elasticity/support)
- Adipose – hypodermis/subcutaneous layer (energy reserve/support/protection)

- Reticular – spleen, lymph nodes (forms framework of organs, binds smooth muscle cells)
- Bone – bones of the skeletal system (mechanical support, blood cell production)
- Blood – blood vessels (transport of substances & gases)
3. muscular: generates force for movement, contracts
locations:
- Skeletal muscle – attached to the skeleton (striated, voluntary)
- Smooth muscle – inside hollow organs (striated, involuntary, intercalated discs)
- Cardiac muscle – located in the heart (not striated, involuntary)
4. nervous: transmit impulses to coordinate activities, receives stimuli
- neurons: specialized cells that are sensitive to various stimuli
- neuroglia: supporting cells that don't generate nerve impulses
locations:
- Nerve cells – located throughout the body
microscope parts:
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)